Is pink Himalayan salt really healthier than regular salt, or is the rosy color just great marketing? Many shoppers pause in the grocery aisle wondering whether those pink crystals offer real nutritional benefits—or simply look prettier on the kitchen counter. Understanding what actually separates Himalayan salt from regular table salt can help you decide which one fits your health goals and daily cooking habits.
Is Pink Himalayan Salt Healthier Than Regular Salt?
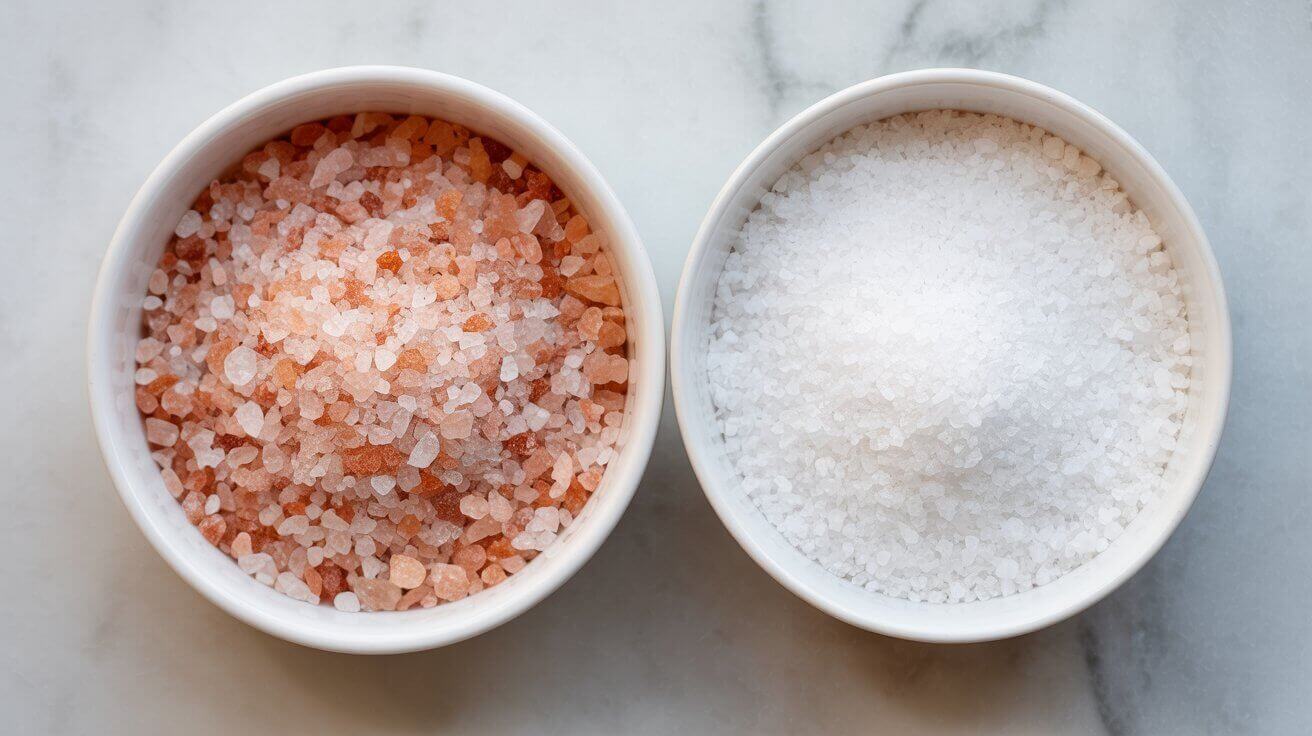
Standing in the grocery aisle, many people compare a bag of pink Himalayan salt with a container of regular table salt, wondering whether the pink version offers any real health benefits. The packaging often hints at purity, minerals, or ancient origins—while regular salt looks familiar and plain.
But what does science actually say? And is pink Himalayan salt truly healthier than regular salt?
More Helpful Reads You Might Like:
What Makes Pink Himalayan Salt Different?
How Pink Salt Is Formed
Pink Himalayan salt comes from ancient deposits in the Himalayan region, mainly in Pakistan. Its rosy color comes from trace minerals such as iron, magnesium, and potassium. These minerals also create a subtle difference in flavor and texture.
Regular table salt comes from underground deposits or seawater. It’s typically processed, purified, and mixed with anti-caking agents. Many brands also add iodine to support thyroid health.
Are There More Minerals in Pink Himalayan Salt?
Pink Himalayan salt is often described as “rich in minerals,” but the mineral content exists only in trace amounts. Scientific analyses show that although dozens of minerals are present, they are far too low to influence health meaningfully.
The biggest nutritional factor in any salt—pink or regular—remains sodium.
Is Pink Himalayan Salt Healthier Than Regular Salt?
What the Research Shows
Despite popular claims, current evidence does not show that pink Himalayan salt is healthier than regular salt. While mineral differences exist, they are nutritionally insignificant unless consumed in amounts far exceeding safe sodium levels.
The body processes sodium the same way regardless of the salt’s color, origin, or crystal size.
Salt and Blood Pressure: What Actually Matters
For people with high blood pressure or heart concerns, total sodium intake matters more than salt type. Pink Himalayan salt is 97–98% sodium chloride—nearly identical to regular table salt.
Major health organizations, including the American Heart Association, recommend reducing overall sodium rather than choosing specialty salts.
Benefits People Notice (and What’s Proven)
Flavor and Texture
Many cooks love the coarse texture and mild mineral-like flavor of pink Himalayan salt. It works well as a finishing salt or for seasoning foods more gently.
These preferences can enhance cooking enjoyment—but they don’t represent proven health benefits.
Additives in Regular Salt
Regular table salt may contain anti-caking agents and typically includes iodine. Individuals who prefer fewer additives might lean toward pink salt.
However, iodized salt remains a key source of iodine. People who avoid seafood, dairy, or eggs may rely on iodized salt to meet daily requirements. Pink Himalayan salt usually lacks added iodine.
Who Should Choose Pink Himalayan Salt?
Taste Preferences & Cooking Style
Some people find pink Himalayan salt less harsh and prefer its appearance. It may also encourage more mindful seasoning.
When Regular Table Salt Is Better
Regular iodized salt is the more practical choice for individuals at risk of iodine deficiency or those who prefer quick-dissolving salt for everyday cooking.
People with thyroid concerns should speak to their doctor before switching exclusively to non-iodized salts.
How Much Salt Is Safe?
U.S. Sodium Guidelines
Most guidelines recommend limiting sodium to under 2,300 mg per day—about one teaspoon of salt. Many people exceed this amount because most sodium comes from processed or restaurant foods, not the salt shaker.
Smart Ways to Reduce Sodium
- Flavor foods with herbs, garlic, citrus, or vinegar
- Choose low-sodium packaged foods
- Compare labels on bread, soups, snacks
- Add salt gradually while cooking
Pink Himalayan salt can be part of a balanced diet, but reducing overall sodium intake is more impactful for health.
Final Thoughts: Which Salt Should You Choose?
Pink Himalayan salt is appealing, flavorful, and aesthetically pleasing. However, the health differences compared with regular salt are small. Its mineral content is too low to produce meaningful benefits, and the sodium impact is essentially identical.
Most people will benefit more from monitoring total sodium intake, using iodized salt when needed, and choosing whichever salt best fits their cooking style.
FAQs
Is pink Himalayan salt better for you than regular salt?
Not based on current evidence. The mineral differences are too small to offer clear health advantages.
Does pink Himalayan salt contain more minerals?
It contains trace minerals, but not in amounts that significantly affect nutrition.
Is Himalayan salt good for high blood pressure?
No. It affects blood pressure similarly to regular table salt because both are mostly sodium chloride.
Is pink Himalayan salt iodized?
No. Most pink salts do not contain added iodine, which is important for thyroid health.
Why is pink salt more expensive?
Mainly due to marketing, perceived purity, and mining processes—not proven health benefits.
Medical Disclaimer: This content is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your physician or a qualified healthcare provider with any questions about a medical condition.
Sources & Further Reading
- Sodium Intake and Cardiovascular Health. National Institutes of Health. PubMed
- American Heart Association — Sodium and Salt
- Harvard Health — The Truth About Salt
- CDC — Sodium and Food Sources
- NIH Office of Dietary Supplements — Iodine Fact Sheet
- Mayo Clinic — Sodium: How to Tame Your Salt Habit