Most people eventually reach a moment—after a doctor’s visit, a family health scare, or simply getting older—when heart health feels deeply personal. One of the first questions that comes up is whether food can genuinely protect the heart. Among all eating patterns studied over the past few decades, one continues to rise above the rest: the Mediterranean diet for heart health.
Many cardiologists recommend this approach because it’s flexible, sustainable, and supported by decades of strong clinical research. Rather than strict rules, it focuses on everyday foods that naturally support cholesterol, blood pressure, and long-term cardiovascular wellness.
More Helpful Reads You Might Like:
Why the Mediterranean Diet Supports Heart Health
Decades of research—including large population studies and randomized trials—link the Mediterranean eating pattern with healthier cholesterol, steadier blood pressure, and lower rates of cardiovascular events.
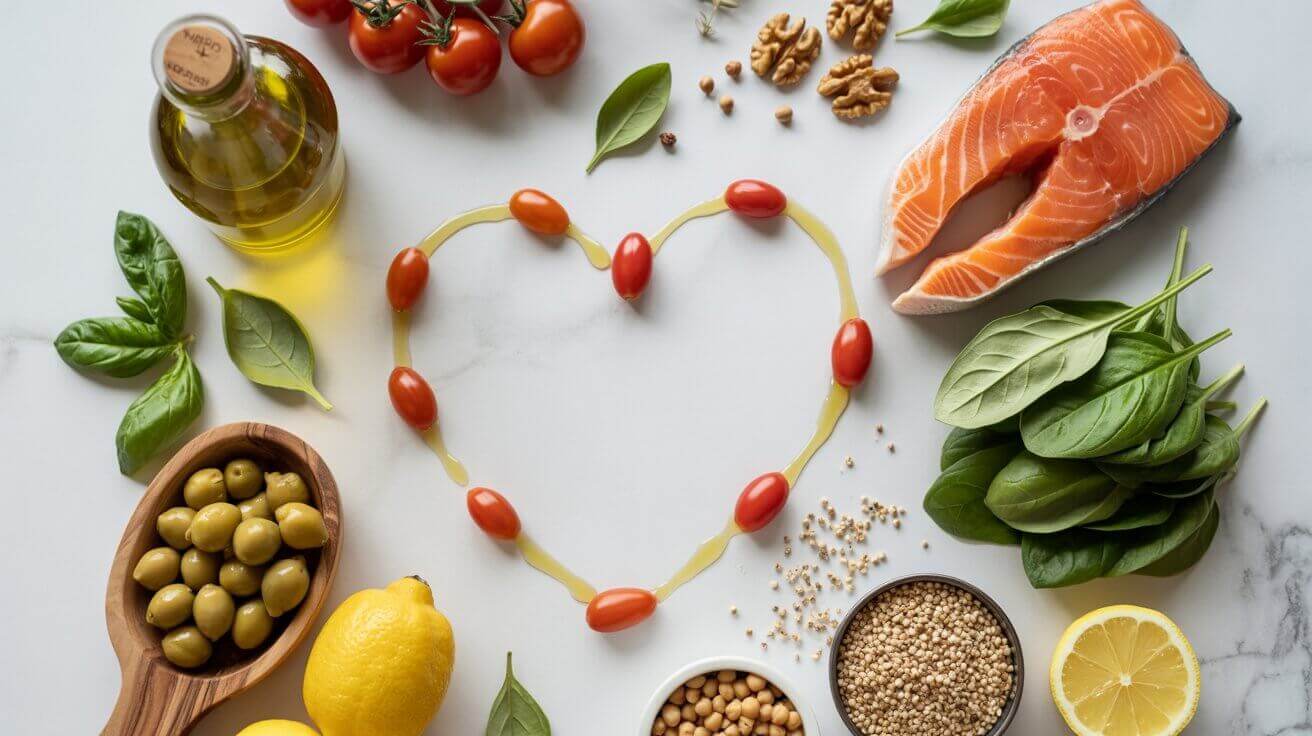
Instead of eliminating entire food groups, this style centers around foods most people already enjoy: fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, beans, seafood, olive oil, and herbs.
Cardiologists often appreciate that it emphasizes eating patterns—not perfection. The long-term blend of healthy fats, plant diversity, and fiber appears to support circulation and overall cardiovascular function.
How It Compares to Other Heart-Healthy Diets
DASH and other heart-focused diets also offer benefits, but the Mediterranean diet stands out for its flexibility.
People find it easier to maintain because it feels natural, flavorful, and satisfying. And sustainability matters: your heart benefits most when healthy choices become a long-term lifestyle.
Key Mediterranean Foods That Protect the Heart
Healthy Fats: Olive Oil, Nuts, and Omega-3 Fish
Healthy fats are the backbone of the Mediterranean diet for heart health.
- Extra-virgin olive oil provides antioxidants and monounsaturated fats that support healthy cholesterol ratios.
- Nuts—like almonds, pistachios, and walnuts—offer steady energy without spiking blood sugar.
- Fatty fish such as salmon, sardines, and trout supply omega-3s, which may reduce inflammation and support blood vessel function.
Cardiology guidelines generally recommend eating seafood at least twice per week.
Fiber-Rich Fruits and Vegetables
Colorful produce delivers fiber, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that help keep the cardiovascular system resilient.
Leafy greens, tomatoes, berries, onions, peppers, and cruciferous vegetables show up repeatedly in Mediterranean meals for their steady, long-term benefits.
Lean Proteins and Plant-Forward Meals
Beans, lentils, chickpeas, tofu, yogurt, poultry, and occasional eggs round out the protein sources. Plant-forward meals—like lentil soup, hummus bowls, or roasted vegetables with olive oil—fit naturally into this eating style.
These meals help support cholesterol balance and healthy blood pressure without feeling restrictive.
How the Mediterranean Diet Supports Cholesterol and Blood Pressure
Improving LDL and HDL Patterns
Research shows that Mediterranean-style eating may help lower LDL (“bad” cholesterol) while supporting healthier HDL levels.
This shift matters because LDL contributes to plaque buildup in arteries over time, while HDL helps remove excess cholesterol.
Reducing Inflammation and Supporting Blood Vessels
Chronic, low-grade inflammation can affect the cardiovascular system.
Foods common in this diet—leafy greens, olive oil, herbs, nuts, and fish—contain natural compounds that help ease inflammation.
At the same time, these foods may improve how blood vessels respond to changes in blood flow, which supports healthier blood pressure.
Simple Ways to Start a Cardiologist-Recommended Mediterranean Diet
Shifting toward this eating pattern doesn’t require an overhaul. Small, consistent steps make the biggest difference.
Easy Breakfast Swaps
- Replace pastries with oatmeal topped with berries and walnuts.
- Try whole-grain toast with avocado, olive oil, and tomatoes.
- Choose Greek yogurt with fruit and a drizzle of honey instead of sugary cereals.
Smarter Grocery Shopping
- Choose extra-virgin olive oil instead of butter for daily cooking.
- Stock up on beans, lentils, nuts, and whole grains like quinoa, farro, and brown rice.
- Add fresh or frozen fish to your weekly cart.
- Fill your basket with colorful produce to make heart-healthy meals easier.
Quick Weeknight Mediterranean Recipes
- Grilled salmon with roasted vegetables and whole grains
- Chickpea and vegetable stew with herbs and olive oil
- Mixed greens salad with tomatoes, cucumbers, olives, and grilled chicken
- Whole-grain pasta with olive oil, garlic, tomatoes, and spinach
These meals highlight the heart-protective benefits of Mediterranean eating while staying practical for busy households.
Early Signs the Mediterranean Diet May Help Your Heart
Some people notice everyday changes after adopting this pattern:
- steadier energy
- improved digestion
- more satisfying meals
- fewer cravings
Over time, this approach may support better cholesterol patterns or smoother blood pressure, though results vary from person to person.
If you have heart disease, diabetes, kidney issues, or other medical concerns, review dietary changes with your clinician.
Final Thoughts
Heart health is shaped by small choices—daily meals, grocery habits, and long-term routines. The Mediterranean diet offers a flexible, flavorful way to support cardiovascular wellness without feeling deprived.
By leaning into olive oil, vegetables, seafood, legumes, and whole grains, you create a foundation your heart can rely on for years ahead. As cardiologists often emphasize: consistency matters more than perfection.
FAQs (Schema-Ready)
1. Is the Mediterranean diet really the best diet for heart health?
Many cardiologists consider it one of the most reliable long-term eating patterns because it consistently supports cholesterol, blood pressure, and inflammation markers.
2. Can the Mediterranean diet lower cholesterol naturally?
Yes. Its mix of healthy fats, fiber, and plant-forward meals often helps improve LDL and HDL levels over time.
3. Is the Mediterranean diet good for high blood pressure?
Studies show improvements in blood vessel function, which can support healthier blood pressure.
4. How long does it take to see benefits?
Some people notice changes in energy or digestion within weeks, while cholesterol and blood pressure shifts usually take a few months.
5. What foods should you avoid on a heart-healthy Mediterranean diet?
Limit processed meats, refined grains, excess sugar, fried foods, and highly processed snacks.
6. Can you follow the Mediterranean diet on a budget?
Absolutely—frozen fish, canned beans, seasonal produce, and whole grains make it affordable.
Medical Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and does not replace personalized medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider with questions about your health or treatment.
Sources & Further Reading
- Estruch R, Ros E, et al. “Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet.” N Engl J Med. 2013.
- American Heart Association – “Mediterranean Diet”
- Mayo Clinic – “Mediterranean Diet: A Heart-Healthy Eating Plan”
- Harvard Health Publishing – “The Mediterranean Diet: Foods That Protect Your Heart”